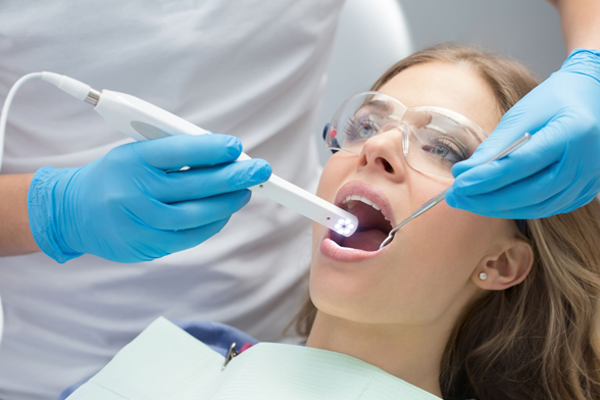
Dental Bonding
Adhesive dentistry deals with adhesion or bonding to the natural substance of enamel, teeth and dentin. On the other hand, direct composite bonding uses tooth-colored dental composites to repair various tooth damages such as cracks or gaps.
Dental bonding is a process in which a tooth-colored resin material is applied and hardened with a special light, which bonds the material to the tooth to restore or enhance person’s smile. This improves the overall appearance of teeth. Tooth bonding techniques have various clinical applications, which includes operative dentistry, preventive dentistry, cosmetic and pediatric dentistry, prosthodontics, and orthodontics.
Who should opt for Dental bonding?
- Decayed teeth
- Chipped or cracked teeth
- Discolored teeth
- Spaces between teeth
- Teeth shaping
- People who need amalgam fillings
Tooth bonding procedure
Anesthesia is not required unless the bonding is being used to fill decayed tooth. Dentists will use a shade guide to select a composite resign color that closely matches the color of tooth. Then, the surface of the tooth will be roughened and a conditioning liquid applied.
These procedures will make the bonding material adhere to the tooth. . The tooth-colored, putty-like resin is then applied, molded, and smoothed to the required shape. An ultraviolet light is used to harden the material. Once the material is hardened, the dentist will shape and polish it to match the sheen of the rest of the tooth surface. Dental bonding takes around 30 to 60 minutes per tooth to complete.
Tooth bonding benefits
Teeth bonding is the easiest and expensive cosmetic dental procedure. The composite resin used in bonding can be shaped and polished to match the natural teeth. Mostly, bonding is used for cosmetic purposes to enhance the appearance of a discolored or chipped tooth. It can be used to fill spaces between teeth and make teeth longer to change the shape or color of teeth. In some cases, bonding is used as a cosmetic alternative to fillings or protects a portion of the tooth’s root which has been exposed due to gum recession.